<%NUMBERING1%>.<%NUMBERING2%>.<%NUMBERING3%> PRTG Manual: IMAP Sensor
The IMAP sensor monitors a mail server using Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).
It can show the following:
- Response time of the mail server
- Number of emails in the defined mailbox
- It can also check the content of emails for certain key words. This way, you can use this sensor to monitor backup solutions via emails that are sent out by these solutions. For more information, see section More.
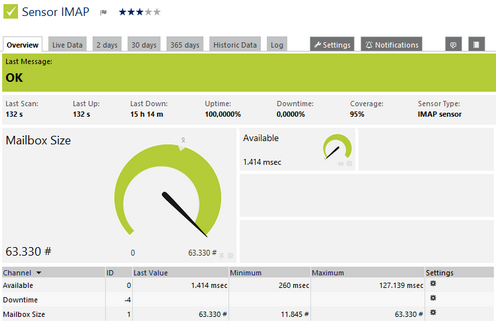
IMAP Sensor
Click here to enlarge: http://media.paessler.com/prtg-screenshots/imap.png
- Note: If you use content checks, we recommend using a dedicated IMAP account that is only checked by PRTG. Editing existing mails in the mailbox of the monitored IMAP account can lead to false alarms or malfunctions of this sensor type.
- Note: This sensor type might not work properly when monitoring sub-folders of mailboxes. If it has to check subsequent emails with identical subjects, later on incoming emails might not be recognized.
- Knowledge Base: My IMAP sensor does not process HTML emails correctly using regex. What can I do?
- Knowledge Base: How can I monitor my backup software to be sure backup succeeded last night?
The Add Sensor dialog appears when adding a new sensor on a device manually. It only shows the setting fields that are imperative for creating the sensor. Therefore, you will not see all setting fields in this dialog. You can change all settings in the sensor's Settings tab later.
On the details page of a sensor, click on the Settings tab to change its settings.
Note: Usually, a sensor connects to the IP Address or DNS Name of the parent device on which you created this sensor. See section Device Settings for details. For some sensor types, you can define the monitoring target explicitly in the sensor settings. Please see below for details about available settings.
Basic Sensor Settings |
|
|---|---|
Sensor Name |
Enter a meaningful name to identify the sensor. By default, PRTG shows this name in the device tree, and in alarms, logs, notifications, reports, maps, libraries, and tickets. |
Tags |
Enter one or more tags, separated by space or comma. You can use tags to group sensors and use tag-filtered views later on. Tags are not case sensitive. We recommend using the default value. You can add additional tags to it, if you like. Other tags are automatically inherited from objects further up in the device tree. Those are not visible here. |
Priority |
Select a priority for the sensor. This setting determines where the sensor is placed in sensor lists. Top priority is at the top of a list. You can choose from one star (low priority) to five stars (top priority). |
IMAP Specific |
|
|---|---|
Timeout (Sec.) |
Enter a timeout in seconds for the request. If the reply takes longer than this value defines, the sensor will cancel the request and show a corresponding error message. Please enter an integer value. The maximum value is 900 seconds (15 minutes). |
Port |
Enter the number of the port that the sensor uses to connect via IMAP. For non-secure connections, usually port 143 is used. For SSL connections it is usually port 993. The actual setting depends on the server you are connecting to. Please enter an integer value. We recommend using the default value. If you do not get a connection, please try another port number. |
Authentication |
|
|---|---|
Username |
Enter a username for IMAP authentication. Please enter a string. |
Password |
Enter a password for IMAP authentication. Please enter a string. |
Transport-Level Security |
|
|---|---|
Sensor Specific |
Define the security level for the sensor connection. Choose between:
If the sensor connects to a server via StartTLS, the connection is established unencrypted first. After the connection is established, the sensor sends a certain command (StartTLS) over the unencrypted connection to negotiate a secure connection via the SSL/TLS protocol. If the sensor uses TLS without StartTLS, the negotiation of a secure connection happens immediately (implicitly) so that no commands are sent in unencrypted plain text. If there is no secure connection possible, no communication will take place. |
Identify Email |
|
|---|---|
Process Email Content |
This sensor can additionally check the content of all incoming emails. Choose between:
|
Mailbox Name |
This field is only visible if you enable email counting or content processing above. Enter the name of the mailbox (for example, the name of the IMAP folder) that the sensor checks. Default value is Inbox. Unless you set a last message date check below, the sensor will always look at all emails contained in the mailbox. Note: Ensure you do not manually edit emails in this mailbox with another email client because this can result in malfunctions of this sensor's email identification. |
Identify by "From" Field |
This option is only visible if you enable email content processing above. Define if you want to check the "From" field of the emails. Choose between:
When using a search, the sensor will scan all emails from the newest to the oldest. Note: The sensor finishes the scan with the first match! This means that after it finds a match in one email, there will be no further checks performed in older emails. |
Search For |
This field is only visible if you enable a "from" check above. Enter a search string using the method defined above. |
Identify by "Subject" Field |
This option is only visible if you enable content processing above. Define if you want to check the "Subject" field of the emails. Choose between:
When using a search, the sensor will scan all emails from the newest to the oldest. Note: The sensor finishes the scan with the first match! This means that after it finds a match in one email, there will be no further checks performed in older emails. |
Search For |
This field is only visible if you enable a "subject" check above. Enter a search string using the method defined above. |
Identify by Mail Body |
This option is only visible if you enable content processing above. Define if you want to check the mail body of the emails. Choose between:
When using a search, the sensor will scan all emails from the newest to the oldest. Note: The sensor finishes the scan with the first match! This means that after it finds a match in one email, there will be no further checks performed in older emails. |
Search For |
This field is only visible if you enable checking the mail body above. Enter a search string using the method defined above. |
Check Last Message Date |
This option is only visible if you enable content processing above. Define if you want to check all emails in the mailbox, or only mails that were received within the last x hours. Choose between:
|
Error Threshold (Hours) |
Enter the maximum age in hours. The sensor processes only emails that are younger. If there is no matching email in the defined time span, the sensor will show a Down status. |
Warning Threshold (Hours) |
Enter the maximum age in hours. The sensor processes only emails that are younger. If there is no matching email in the defined time span, the sensor will show a Warning status. |
Sensor Behavior |
|
|---|---|
Set to Error |
This setting is only visible if you enable email content check above. Define in which cases the sensor will show a Down status. Choose between:
|
Check Method |
This setting is only visible if you select an if-condition above. Define how you want to check for the above condition. Choose between:
When using a search, the sensor will scan all emails from the newest to the oldest. Note: The sensor finished the scan with the first match! This means that after it finds a match in one email, there will be no further checks performed in older emails. |
Search Text |
This setting is only visible if you select an if-condition above. Enter a search string using the method defined above. |
Error Message |
This setting is only visible if you select an alarm condition above. Define the message that the sensor will show for a Down status. |
Set to Warning |
This setting is only visible if you enable content check above. Define in which cases the sensor will show a Warning status. Choose between:
|
Check Method |
This setting is only visible if you select an if-condition above. Define how you want to check for the above condition. Choose between:
When using a search, the sensor will scan all emails from the newest to the oldest. Note: The sensor finishes the scan with the first match! This means that after it finds a match in one email, there will be no further checks performed in older emails. |
Search Text |
This setting is only visible if you enable an if-condition above. Enter a search string using the method defined above. |
Warning Message |
This setting is only visible if you select a warning condition above. Define the message that the sensor will show for a Warning status. |
No Matching Mail Behavior |
This setting is only visible if you enable content check above. Define how the sensor will react if it does not find matching emails in the mailbox that it scans. Choose between:
|
Message |
This field is only visible if you enable a no matching behavior above. Define the message that the sensor will show if it did not find any matching emails together with a Warning or Down status as you define above. |
Sensor Result |
Define what PRTG will do with the result of the sensor. Choose between:
|
Sensor Display |
|
|---|---|
Primary Channel |
Select a channel from the list to define it as the primary channel. In the device tree, the last value of the primary channel will always be displayed underneath the sensor's name. The available options depend on what channels are available for this sensor. Note: You can set another primary channel later by clicking on the pin symbol of a channel in the sensor's overview tab. |
Chart Type |
Define how different channels will be shown for this sensor.
|
Stack Unit |
This setting is only available if stacked graphs are selected above. Choose a unit from the list. All channels with this unit will be stacked on top of each other. By default, you cannot exclude single channels from stacking, if they use the selected unit. However, there is an advanced procedure to do so. |
By default, all following settings are inherited from objects higher in the hierarchy and should be changed there, if necessary. Often, best practice is to change them centrally in the Root group's settings. To change a setting for this object, disable inheritance by clicking on the check mark symbol in front of the respective setting name. You will then see the options described below.
Scanning Interval |
|
Scanning Interval |
Select a scanning interval (seconds, minutes, or hours) from the list. The scanning interval determines the time the sensor waits between two scans. You can change the available intervals in the system administration. |
When a Sensor Reports an Error |
Define the number of scanning intervals a sensor has to report an error until the sensor will be set to a Down status. The sensor can try reaching a device several times, depending on your setup you can specify here, to help avoid false alarms if the monitored device has only temporary issues. For previous scanning intervals with failed requests, the sensor will show a Warning status. Choose between:
Note: Sensors that monitor via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) always wait at least one scanning interval until they show an error. It is not possible to set a WMI sensor "down" immediately, so the first option will not apply to these sensor types (all other options can apply). Note: If a sensor has defined error limits for channels, this sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" option will apply. Note: If a channel uses lookup values, the sensor will always be set to a Down status immediately, so no "wait" options will apply. |
Schedules, Dependencies, and Maintenance Window |
|
|---|---|
Note: Inheritance for schedules, dependencies, and maintenance windows cannot be interrupted; the according settings from the parent objects will always be active. However, you can define additional settings here. They will be active in parallel to the parent objects' settings. |
|
Schedule |
Select a schedule from the list. Schedules can be used to monitor for a certain time span (days, hours) throughout the week. With the period list option it is also possible to pause monitoring for a specific time span. You can create new schedules and edit existing ones in the account settings. Note: Schedules are generally inherited. New schedules will be added to existing ones, so all schedules are active. |
Maintenance Window |
Specify if you want to set-up a one-time maintenance window. During a maintenance window this object and all child objects will not be monitored. They will enter a paused state then. Choose between:
Note: To terminate a current maintenance window before the defined end date, you can change the time in Maintenance End At field to a date in the past. |
Maintenance Begins At |
This field is only visible if maintenance window is enabled above. Use the date time picker to enter the start date and time of the maintenance window. |
Maintenance End At |
This field is only visible if maintenance window is enabled above. Use the date time picker to enter the end date and time of the maintenance window. |
Dependency Type |
Define a dependency type. Dependencies can be used to pause monitoring for an object depending on the status of another. You can choose between:
Note: Testing your dependencies is easy! Simply choose Simulate Error Status from the context menu of an object that other objects depend on. A few seconds later all dependent objects should be paused. You can check all dependencies in your PRTG installation by selecting Devices | Dependencies from the main menu bar. |
Dependency |
This field is only visible if the select object option is enabled above. Click on the reading-glass symbol and use the object selector to choose an object on which the current sensor will be dependent on. |
Delay (Seconds) |
Define a time span. After the master object for this dependency comes back to an Up status, monitoring of the depending objects will be additionally delayed by the defined time span. This can help avoid false alarms, for example, after a server restart, by giving systems more time for all services to start up. Please enter an integer value in seconds. Note: This setting is not available if you choose this sensor to be the Master object for parent. In this case, please define delays in the parent Device Settings or the superior Group Settings. |
Access Rights |
|
User Group Access |
Define which user group(s) will have access to the object you're editing. A table with user groups and right is shown; it contains all user groups from your setup. For each user group you can choose from the following access rights:
You can create new user groups in the System Administration—User Groups settings. To automatically set all objects further down in the hierarchy to inherit this object's access rights, set a check mark for the Revert children's access rights to inherited option. For more details about access rights, please see section User Access Rights. |
Knowledge Base: How can I monitor my backup software to be sure backup succeeded last night?
Knowledge Base: My IMAP sensor does not process HTML emails correctly using regex. What can I do?
To change display settings, spike filter, and limits, switch to the sensor's Overview tab and click the gear icon of a specific channel. For detailed information, please see Sensor Channels Settings section.
Click the Notifications tab to change notification triggers. For detailed information, please see Sensor Notifications Settings section.
For more general information about settings, please see Object Settings section.
For information about sensor settings, please see the following sections:
Keywords: